Rotary die cutting is a method used in manufacturing to cut and shape materials efficiently. An industrial rotary die cutter is a tool that can precisely cut materials like labels with speed. Various industries, including healthcare, automotive, packaging, and labeling, utilize rotary die-cutting to produce their goods.
But what exactly is a rotary die-cutter? How does it differ from other die-cutting methods? And when is it best to use? Keep reading to discover all you need to know about rotary die cutters.
1. What is Rotary Die Cutting?
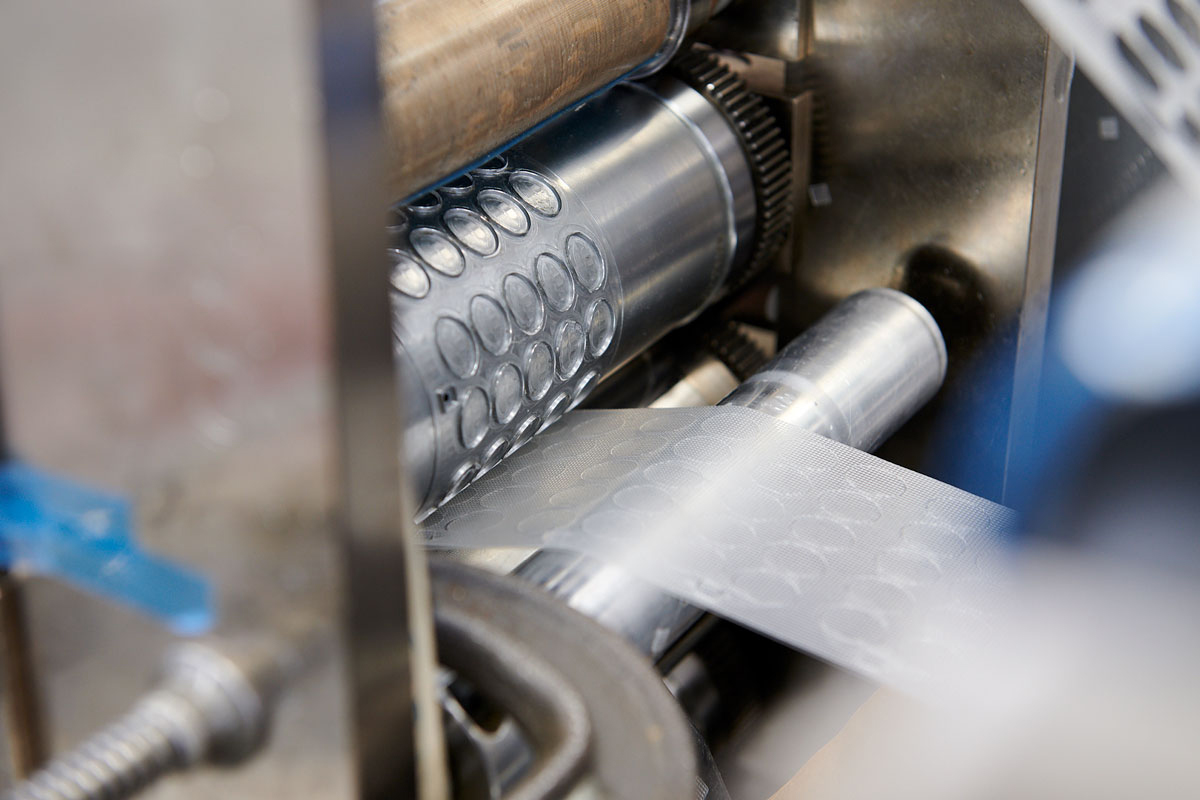
Rotary die cutting is a versatile and efficient method commonly used in label manufacturing. In this process, a cylindrical die equipped with sharp blades or creasing lines is employed by a rotary die cutter. As the material passes through the machine, the rotary die rotates to precisely cut the labels or other items. While this technique is ideal for creating custom labels, it can also be applied to produce various products like bandages, gaskets, and paper items.
2. Features of Industrial Rotary Die Cutters
The industrial rotary die cutter is a specialized piece of equipment tailored for rotary die-cutting applications. These machines are built for robust, continuous production. Here are some key features of an industrial rotary die cutter:
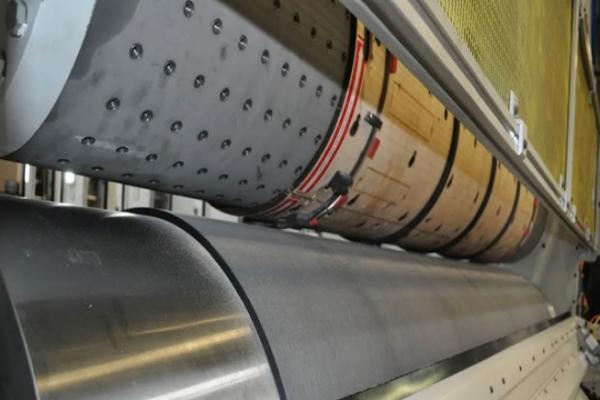
1) Rotary Die Cylinder
The rotary die cylinder is a crucial element of the rotary die cutter. It is a cylindrical tool equipped with sharp blades, creasing lines, or other cutting components.
2) Anvil Cylinder
The anvil cylinder is another vital part of the rotary die cutter. It offers support and pressure to ensure clean and precise cuts. The material passes between the rotary die and the anvil during the cutting process. The clearance between the anvil and the rotary die can be adjusted to apply the correct amount of pressure.
3) Material Handling
Industrial rotary die cutters utilize feeding and tension control systems to facilitate smooth material movement through the machine. A roll of material is loaded into the machine, which then feeds the material through the die-cutting station.
3. The Rotary Die Cutting Process
Now that you know more about rotary die-cutters, let’s examine the process of die-cutting in detail.
- The process commences with a roll of material being unwound and fed into the machine.
- Before production kicks off, the die is configured to match the label’s specific shape and size. This is where features like perforations or scores are set up.
- During the process of moving through the machine, the material passes between the anvil roll and the rotary die. Both the rotary die and anvil rotate in opposite directions. The die’s blades come into contact with the material, cutting or shaping it.
- Any excess material or waste produced during the process is typically eliminated at this stage. Many machines are equipped with vacuum systems or stripping stations to clear away the extra material without halting the process.
- Finally, the completed labels are either wound onto another roll or cut into individual sheets, based on the client’s requirements.
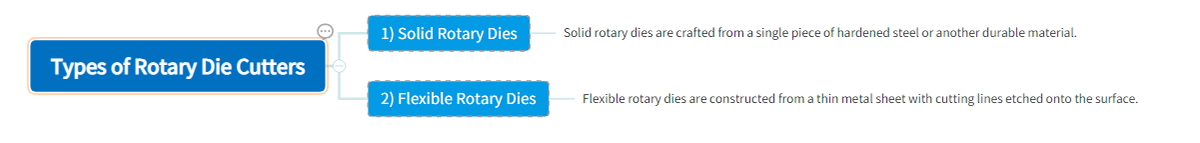
4. Types of Rotary Die Cutters
Rotating die cutting is very flexible and versatile, which is one of its biggest advantages. It is possible to cut custom shapes from a variety of materials using rotary die cutters. This versatility is enabled by the rotary die. Generally speaking, there are two types of rotary dies: solid and flexible. Rotating dies have different advantages and disadvantages, so selecting the right one is important.
1) Solid Rotary Dies
Solid rotary dies are crafted from a single piece of hardened steel or another durable material. They boast a long lifespan and can be sharpened when necessary. While solid rotary dies come with a higher price tag, their durability often justifies the investment. However, the process of changing solid rotary dies can be time-consuming, leading to longer lead times compared to flexible dies.
2) Flexible Rotary Dies
Flexible rotary dies are constructed from a thin metal sheet with cutting lines etched onto the surface. These dies are held in place by a magnetic cylinder, allowing them to cut or perforate materials. Flexible rotary dies are cost-effective and can be manufactured swiftly.
Nonetheless, the magnetic cylinders required to secure them can be expensive. Each size and circumference necessitate a separate cylinder, adding to the overall cost. Despite the initial expenses, replacing worn-out flexible rotary dies is budget-friendly in the long run.
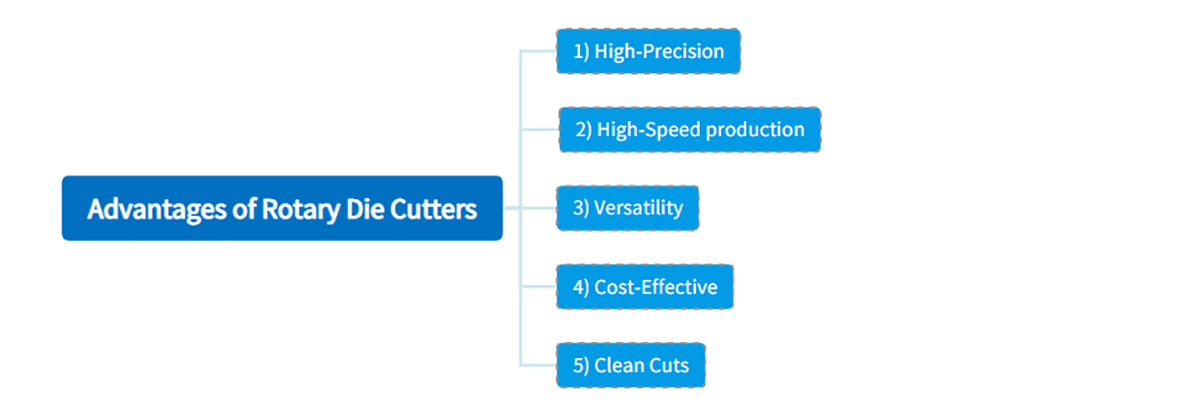
5. Advantages of Rotary Die Cutters
In some cases, you may use more than one die-cutting method for the same project, but rotary die cutters offer several advantages that place them above other types:
1) High-Precision
Rotary die cutting ensures accurate and uniform cuts, resulting in identical labels and products.
2) High-Speed production
This method offers fast and continuous production, making it ideal for high-volume label manufacturing.
3) Versatility
Customization is simple with rotary die cutters, allowing for a diverse range of label shapes, sizes, and designs.
4) Cost-Effective
By minimizing material wastage, rotary die cutting proves to be cost-efficient for large production runs.
5) Clean Cuts
Rotary dies deliver clean and sharp edges on labels, enhancing the overall appearance of the final product.
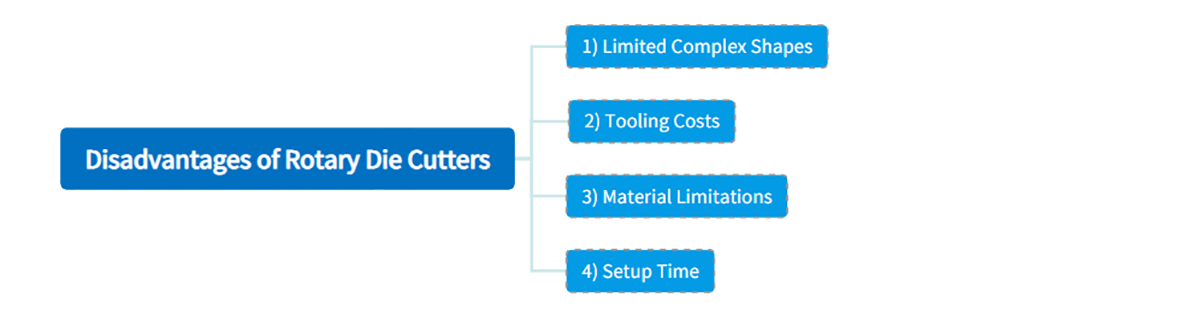
6. Disadvantages of Rotary Die Cutters
While rotary die cutters offer numerous advantages, it’s essential to consider their limitations as well. Here are some disadvantages of rotary die cutters:
1) Limited Complex Shapes
Rotary die cutting may not be suitable for highly intricate shapes or designs, particularly those with interior cuts. In such cases, laser cutting might be a more suitable option.
2) Tooling Costs
Creating custom rotary dies, especially solid ones, can incur significant expenses. While the cost may be justified for high-volume runs, it may not be as cost-effective for small runs or products with frequent design changes.
3) Material Limitations
Rotary die cutting is not as effective for cutting rigid or thick materials due to its operational mechanism. In such instances, flatbed cutting may be a more suitable alternative.
4) Setup Time
Setting up a rotary die-cutting machine for a new job can be time-intensive, especially when changing dies or adjusting for different materials. However, flexible rotary dies offer quicker setup times compared to solid rotary dies.
7. Top Considerations for the Rotary Die Cutting Process
Despite the benefits of rotary die cutting, there are several considerations to take into account before using it.
1) Size Constraints
The effectiveness of rotary die cutting is influenced by the dimensions of the materials, including height, length, and width. Other die cutting methods may be more suitable for larger finished products.
2) Thickness
Thicker materials may not be well-suited for the rotary die cutting process.
3) Volume
For low-volume orders or prototype runs, rotary die cutting may not offer the most cost-effective solution.
4) Tonnage
High tonnage die cutting requirements may not align well with the capabilities of the rotary die cutting process.
5) Best for Materials on a Roll
While sheets of materials can be processed through rotary dies, optimal efficiency is achieved when materials are supplied in the form of a continuous roll.
8. Rotary Die Cutters Maintenance Tips
Today’s rotary die cutting machines are designed to deliver precise and accurate cuts through materials like film, paper, or tag stock. These dies can endure millions of revolutions, showcasing their high-volume capacity. To ensure consistent performance, routine maintenance is key to address any minor issues promptly and maintain operational efficiency.
Even top-quality rotary cutting dies experience wear and tear over time. Neglecting regular maintenance can escalate minor issues into major downtime problems. Running a die-cutter beyond its recommended resharpening schedule can lead to complications.
Unplanned downtime can significantly impact your business’s profitability. By proactively monitoring your die cutting operations and implementing preventive measures, you can prolong the lifespan of your die-cutter. Here are some essential maintenance practices for your die cutting machine.
1) Cleaning
To maintain optimal performance of your die-cutter, it’s crucial to clean it thoroughly after each run. Make sure to remove substrate fibers, adhesive, and ink residue from key components like:
- Rotary die body and blades: It is recommended not to use metal tools for adhesive removal, wooden tools are highly suggested due to less of a chance to damage blades. Chemical cleaners must not exceed a PH 10, it could pit blade tips or remove proprietary coatings due to acidity.
- Anvil cylinders: Clean the surface and check for scratches or dents. Regularly inspect the bearer area for wear and ensure it is well lubricated.
- Bearer areas on both dies and anvils: These areas influence cut quality, so keep them clean and properly lubricated.
- Gears: Regularly inspect and clean gears to prevent the buildup of oil and paper dust in the teeth, which can lead to registration issues.
Excessive adhesive buildup on the rotary die can impact machine performance, causing issues like deep die strikes or label lifting. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to prevent such inaccuracies and ensure the smooth operation of your die-cutter.
2) Alignment and Calibration
Maintaining proper alignment and calibration is crucial for the optimal performance of your die-cutting machine. Over time, factors like debris buildup, wear and tear, or other external factors can affect the machine’s precision in registration and cut quality.
To address this, we suggest conducting a quality assurance (QA) test during scheduled maintenance checks or periodically during downtime. This test should involve checking the gaps of all magnetic cylinders every six months, documenting any changes in values, and conducting regular inspections of bearings and die stations. By staying proactive with these checks, you can ensure that your machine operates at its best capacity.
3) Storage
Proper storage is a crucial aspect of die-cutter maintenance to safeguard the condition and performance of your dies. After cleaning, ensure that each die is stored securely to prevent accidental damage or exposure to harmful elements.
Consider wrapping the dies in oil paper and storing them in protective hanging bags, cardboard rolls, flat boxes, or designated storage containers like our recognizable blue boxes. Whether you use solid cutting dies or flexible ones, apply a light coating of acid-free oil before storing them.
Failure to store dies correctly can result in damage or premature dullness, leading to costly repairs or replacements. By following proper storage practices, you can avoid unnecessary expenses and downtime, ensuring your dies remain in top condition for future use.
4) Handling
Proper handling of dies is essential to maintain their quality and effectiveness. Mishandling, such as bending a flexible die or placing the die blade side down, can lead to damage to the blades or cylinders. Incorrect handling not only compromises the die’s performance but can also pose safety risks in extreme cases. Be sure to handle diseases with care and attention to preserve their integrity and ensure safe operation.
9. Conclusion
In summary, rotary die cutting is a valuable manufacturing process with broad applications across various industries. Whether opting for solid or flexible rotary dies, understanding the process’s intricacies, benefits, and limitations is key to making informed decisions for your business. The precision, speed, and customization capabilities of rotary die cutting make it particularly advantageous for high-volume production needs, especially in sectors like healthcare, automotive, and packaging.
To maximize the efficiency and accuracy of your rotary die-cutting equipment, proper maintenance is paramount. Regular cleaning, alignment checks, calibration, and correct handling and storage practices are essential to prevent downtime and costly repairs, ensuring smooth and productive operations. By following these maintenance guidelines and selecting the most suitable die-cutting methods for your production requirements, you can enhance your manufacturing process and achieve consistent, top-quality outcomes.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.